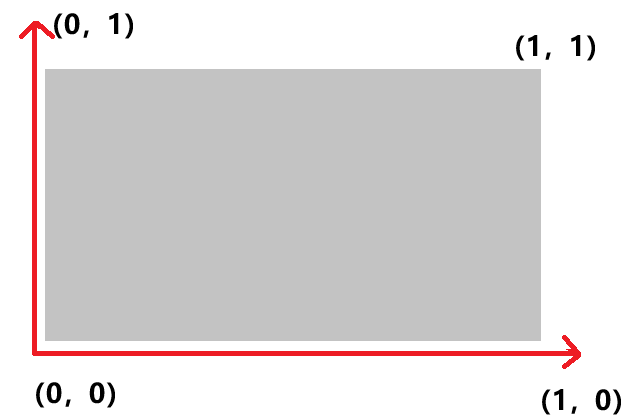
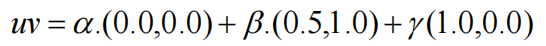void Raster::rasterizeTriangle(
std::vector<Point>& results,
const Point& v0,
const Point& v1,
const Point& v2) {
int maxX = static_cast<int>(std::max(v0.x, std::max(v1.x, v2.x)));
int minX = static_cast<int>(std::min(v0.x, std::min(v1.x, v2.x)));
int maxY = static_cast<int>(std::max(v0.y, std::max(v1.y, v2.y)));
int minY = static_cast<int>(std::min(v0.y, std::min(v1.y, v2.y)));
math::vec2f pv0, pv1, pv2;
Point result;
for (int i = minX; i <= maxX; ++i) {
for (int j = minY; j <= maxY; ++j) {
pv0 = math::vec2f(v0.x - i, v0.y - j);
pv1 = math::vec2f(v1.x - i, v1.y - j);
pv2 = math::vec2f(v2.x - i, v2.y - j);
auto cross1 = math::cross(pv0, pv1);
auto cross2 = math::cross(pv1, pv2);
auto cross3 = math::cross(pv2, pv0);
bool negativeAll = cross1 < 0 && cross2 < 0 && cross3 < 0;
bool positiveAll = cross1 > 0 && cross2 > 0 && cross3 > 0;
if (negativeAll || positiveAll) {
result.x = i;
result.y = j;
interpolantTriangle(v0, v1, v2, result);
results.push_back(result);
}
}
}
}
void Raster::interpolantTriangle(const Point& v0, const Point& v1, const Point& v2, Point& p) {
auto e1 = math::vec2f(v1.x - v0.x, v1.y - v0.y);
auto e2 = math::vec2f(v2.x - v0.x, v2.y - v0.y);
float sumArea = std::abs(math::cross(e1, e2));
auto pv0 = math::vec2f(v0.x - p.x, v0.y - p.y);
auto pv1 = math::vec2f(v1.x - p.x, v1.y - p.y);
auto pv2 = math::vec2f(v2.x - p.x, v2.y - p.y);
float v0Area = std::abs(math::cross(pv1, pv2));
float v1Area = std::abs(math::cross(pv0, pv2));
float v2Area = std::abs(math::cross(pv0, pv1));
float weight0 = v0Area / sumArea;
float weight1 = v1Area / sumArea;
float weight2 = v2Area / sumArea;
p.color = lerpRGBA(v0.color, v1.color, v2.color, weight0, weight1, weight2);
p.uv = lerpUV(v0.uv, v1.uv, v2.uv, weight0, weight1, weight2);
}
RGBA Raster::lerpRGBA(const RGBA& c0, const RGBA& c1, const RGBA& c2, float weight0, float weight1, float weight2) {
RGBA result;
result.mR = static_cast<float>(c0.mR) * weight0 + static_cast<float>(c1.mR) * weight1 + static_cast<float>(c2.mR) * weight2;
result.mG = static_cast<float>(c0.mG) * weight0 + static_cast<float>(c1.mG) * weight1 + static_cast<float>(c2.mG) * weight2;
result.mB = static_cast<float>(c0.mB) * weight0 + static_cast<float>(c1.mB) * weight1 + static_cast<float>(c2.mB) * weight2;
result.mA = static_cast<float>(c0.mA) * weight0 + static_cast<float>(c1.mA) * weight1 + static_cast<float>(c2.mA) * weight2;
return result;
}
math::vec2f Raster::lerpUV(const math::vec2f& uv0, const math::vec2f& uv1, const math::vec2f& uv2, float weight0, float weight1, float weight2) {
math::vec2f uv;
uv = uv0 * weight0 + uv1 * weight1 + uv2 * weight2;
return uv;
}
|